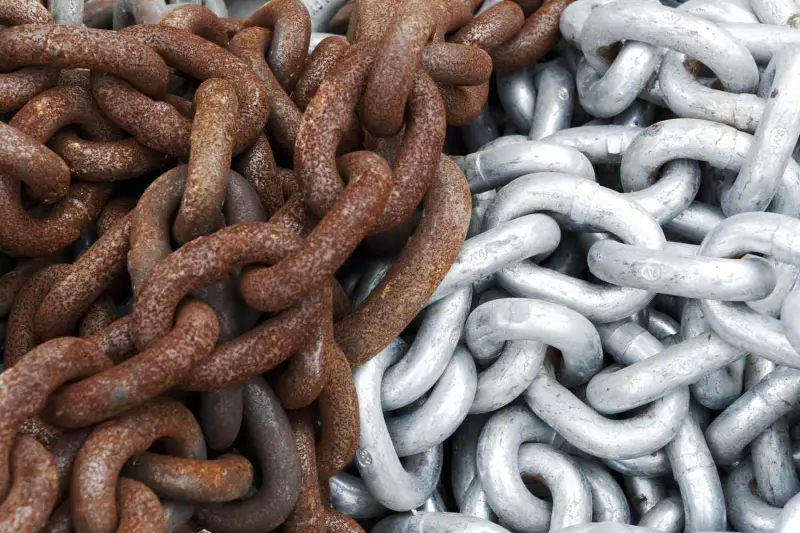
Rust, also known as corrosion, is a chemical process that occurs when metal is exposed to air and moisture. It is a type of oxidation reaction that involves the transfer of electrons between the metal and the surrounding environment. When iron or steel, which are commonly used in construction and manufacturing, are exposed to oxygen and water, they react to form iron oxide, or rust.
The process of rusting involves the following steps:
- The metal surface is exposed to water, which dissolves oxygen from the air to form a thin layer of water and oxygen molecules.
- The oxygen molecules react with the metal surface to form metal oxide.
- The metal oxide then reacts with more water and oxygen to form rust, which is a complex mixture of iron oxide and other compounds.
Rust is a common problem that can occur in a wide range of metal objects and surfaces, such as cars, bikes, tools, and outdoor furniture. It can weaken and deteriorate metal, which can lead to safety hazards and costly repairs. Preventing rust is important to maintain the integrity and longevity of metal objects. This can be done through various methods, including applying protective coatings, using rust inhibitors, and keeping metal objects dry and clean.
Preventing Rust
Preventing rust is important for several reasons, including:
- Maintaining the Appearance: Rust can make metal objects and surfaces look unsightly, which can decrease their aesthetic value. This is particularly important for items that are visible or used frequently, such as cars, bikes, and outdoor furniture.
- Preserving Structural Integrity: Rust can weaken metal objects and surfaces, which can compromise their structural integrity. This can be particularly concerning for objects that are used in safety-critical applications, such as bridges, airplanes, and heavy machinery. If rust is allowed to progress unchecked, it can eventually lead to catastrophic failure.
- Reducing Maintenance Costs: Repairing or replacing rusted metal objects can be expensive, particularly if the rust has caused significant damage. Preventing rust can help to reduce maintenance costs by extending the life of metal objects and reducing the need for repairs.
- Enhancing Safety: Rust can create safety hazards by weakening metal objects and surfaces, causing them to break or fail unexpectedly. This can be particularly dangerous in situations where people are working or interacting with the objects, such as in construction sites or industrial settings.
There are several methods for preventing rust, including:
- Applying Protective Coatings: Coatings such as paint, varnish, and wax can help to protect metal objects from exposure to air and moisture. These coatings create a barrier that prevents water and oxygen from coming into contact with the metal surface.
- Using Rust Inhibitors: Rust inhibitors are chemicals that can be applied to metal surfaces to prevent rust from forming. They work by forming a protective layer on the metal surface that prevents water and oxygen from reacting with the metal.
- Keeping Metal Objects Dry and Clean: Rust requires moisture to form, so keeping metal objects dry can help to prevent rust. It is also important to keep metal objects clean, as dirt and debris can trap moisture against the metal surface, accelerating the rusting process.
In summary, preventing rust is important for maintaining the appearance, structural integrity, and safety of metal objects and surfaces, as well as reducing maintenance costs. Various methods can be used to prevent rust, including applying protective coatings, using rust inhibitors, and keeping metal objects dry and clean.
What Is Rust: Comparison Table
Rust is a corrosion problem that affects metal surfaces and can lead to significant damage over time. It is caused by the reaction of metal with oxygen and moisture in the air, resulting in the formation of iron oxide (rust). This corrosion can weaken the structure of the metal and cause it to break or fail.
Methods for Solving Rust
- Sanding and wire brushing: This method involves removing the rust by sanding or wire brushing the affected surface. This is a relatively simple and inexpensive method, but it can be time-consuming and may not remove all of the rust.
- Chemical rust removers: Chemical rust removers are available in liquid or gel form and are applied to the affected surface. They work by dissolving the rust and can be effective for removing rust from small areas. However, they can be hazardous to use and can damage surrounding surfaces if not used carefully.
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis is a process that uses an electrical current to remove rust from metal surfaces. It involves immersing the metal in an electrolyte solution and applying an electrical current to the metal. This causes the rust to break down and dissolve, leaving a clean metal surface.
- Blasting: Blasting involves using high-pressure air or abrasive materials to remove rust from metal surfaces. This method is effective for removing rust from large surfaces, but it can be messy and requires specialized equipment.
- Painting or coating: This method involves covering the affected surface with paint or another protective coating. This can help to prevent further rust from forming and can provide a cosmetic solution to the problem.
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Sanding and wire brushing | Inexpensive, readily available tools | Time-consuming, may not remove all rust |
| Chemical rust removers | Effective for small areas, readily available | Hazardous, can damage surrounding surfaces |
| Electrolysis | Effective for removing rust, leaves clean metal surface | Requires specialized equipment and setup |
| Blasting | Effective for large surfaces, fast and efficient | Messy, requires specialized equipment |
| Painting or coating | Prevents further rust from forming, cosmetic solution | Does not remove existing rust, requires regular maintenance |
Each method for solving rust has its own pros and cons, and the best method for you will depend on the extent of the rust problem, the type of metal, and the resources and equipment available. If you have a small area with light rust, sanding or wire brushing may be sufficient. For larger areas or more severe rust problems, electrolysis or blasting may be the best option. If you’re looking for a cosmetic solution, painting or coating can be a good choice. Regardless of the method you choose, it’s important to act promptly to prevent further rust from forming.

Equipment To Work With Rust
| Equipment | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Sandpaper | Coarse or fine grit paper used for sanding | Removing rust by sanding |
| Wire brush | A brush with wire bristles used for removing rust | Removing rust by brushing |
| Chemical rust remover | A liquid or gel chemical solution used to dissolve rust | Removing rust with chemicals |
| Electrolysis setup | A setup including a power source, electrolyte solution, and metal electrodes | Removing rust using electrolysis |
| Blasting equipment | High-pressure air or abrasive material blasting equipment | Removing rust with blasting |
| Paint or coating | Paint or other protective coating used to cover rust | Preventing further rust and providing a cosmetic solution |
| Protective gear | Gloves, goggles, and other protective gear to protect from chemicals or debris | Protecting yourself while using hazardous chemicals or working with abrasive materials |
Note: This list is not exhaustive and may vary depending on the specific needs and circumstances of your project. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions and follow proper safety procedures when using any equipment.
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Identify the extent of the rust problem: Look for areas of rust on metal surfaces, and assess the extent of the problem. Consider the type of metal, the location of the rust, and the resources and equipment available.
- Choose the appropriate method: Based on the extent of the rust problem, choose the method that is best for you. Options include sanding and wire brushing, chemical rust removers, electrolysis, blasting, or painting or coating.
- Prepare the surface: Clean the surface of the metal to be treated, removing any dirt or debris. For chemical rust removers, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for preparing the surface.
- Apply the method: Depending on the method chosen, apply the sandpaper, wire brush, chemical rust remover, or paint or coating as instructed. For electrolysis, set up the equipment according to the manufacturer’s instructions and immerse the metal in the electrolyte solution. For blasting, use the equipment to remove the rust.
- Check for effectiveness: After applying the method, inspect the surface to ensure that the rust has been effectively removed or prevented. Repeat the process as needed.
- Finish and protect: Once the rust has been removed or prevented, finish the surface as desired. For example, apply a coat of paint or another protective coating to prevent further rust from forming.
Note: Always follow proper safety procedures and manufacturer’s instructions when using any equipment or chemicals. Wear gloves, goggles, and other protective gear as necessary to protect yourself while working with hazardous materials.
By following these steps, you can effectively solve rust problems and prevent further damage to metal surfaces. Good luck!

F.A.Q.
What is rust?
Rust is a chemical process that occurs when iron reacts with moisture and oxygen, resulting in the formation of iron oxide, commonly known as rust. Rust can cause metal surfaces to deteriorate and weaken over time, leading to potential failure or corrosion.
What causes rust to form?
Rust forms as a result of the oxidation of iron in the presence of moisture and air. This can happen when metal surfaces are exposed to water, humidity, or other moisture sources.
How do I remove rust?
There are several methods for removing rust, including sanding and wire brushing, chemical rust removers, electrolysis, blasting, and painting or coating. The best method depends on the extent of the rust problem, the type of metal, and the resources and equipment available.
Can I prevent rust from forming?
Yes, you can prevent rust from forming by keeping metal surfaces dry, applying protective coatings, such as paint or rust inhibitors, and storing metal objects in a dry, well-ventilated place.
Is rust harmful to human health?
In most cases, rust is not harmful to human health. However, some chemical rust removers can be hazardous if ingested or if they come into contact with the skin. It’s important to always follow manufacturer’s instructions and proper safety procedures when using chemical rust removers.
Can I paint over rust?
Yes, you can paint over rust, but it is important to remove as much rust as possible before painting to ensure that the paint will adhere properly. In some cases, a rust inhibitor may need to be applied before painting to prevent further rust from forming.


Leave a Reply